In continuation of my blog series on Evaluating Immersive Technologies, today I present a look at the limitations of Holograms. If you have yet read my previous posts, check them out here:
- A Beginner’s Guide to the Immersive World
- Part 1: Limitations of Virtual Reality
- Part 2: Limitations of Augmented Reality
- Part 3: Limitations of Mixed Reality
Understanding Holography
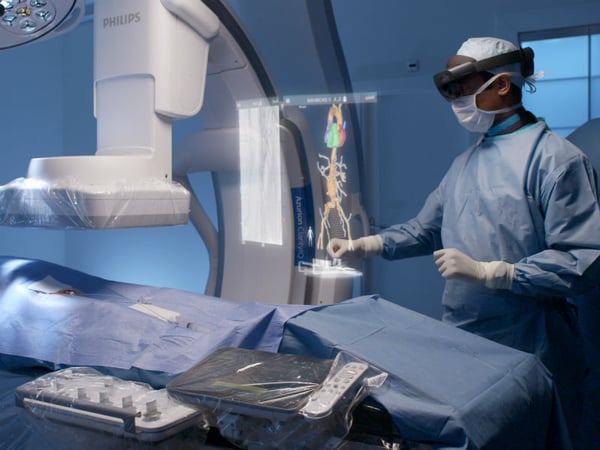
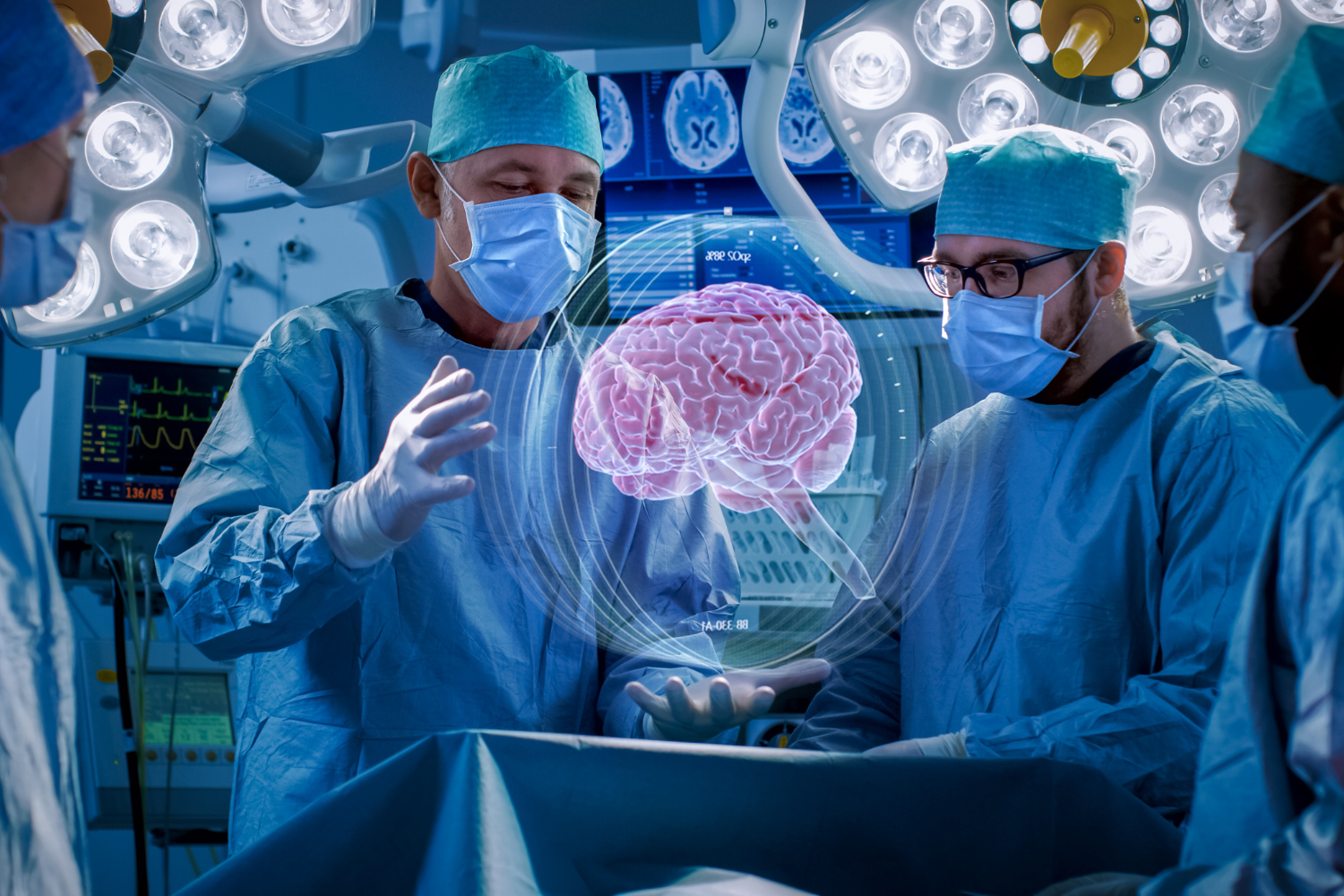
Holograms are 3D images that are typically created using laser technology, but other methods are currently in development. They can be viewed without the need for special glasses or headsets and provide a highly realistic and interactive experience. Holograms are used in various applications such as entertainment, marketing, and education.
Current readily available hologram technology requires viewing glasses and is limited by resolution and color limitations making it difficult to create highly realistic and immersive experiences. I want to also note there are some new hologram technologies that I have been working with that overcome these resolution and color limitations, and don’t require a headset and I foresee that holograms will soon become more viable.
Enterprise Use Cases for Holography
Healthcare: Holography is being used for medical imaging, surgical planning, and training purposes. Patient holograms can be used to train medical staff to minimize errors and prepare for difficult procedures.
Architecture & Construction: Holographic technology is used to project designs and visualizations to understand how structures will look once built or used to plan and coordinate construction tasks.
Manufacturing: Holography can be used for a variety of reasons, including prototyping, quality control, assembly, and training purposes. Digital twins can be used in the prototyping phase to understand how products will interact, behave, and be utilized by teams.
Limitations of Hologram Technology
Holograms that are limited in their resolution and color capabilities can affect the quality of the image and the level of realism that can be achieved. The current technology used to create holograms has limitations in terms of the number of pixels that can be displayed, which affects the level of detail that can be seen. Also, holograms are often limited in their color range, resulting in a lack of color accuracy and vibrancy.
Holograms are typically limited in their size and viewing angle, which can affect the level of immersion that can be achieved. While advancements have been made in creating larger holographic displays, these displays can be expensive and difficult to produce.
- Limited resolution: Holograms with limited resolution can reduce the quality and realism of the image.
- User interface: The hologram system should have an intuitive and user-friendly interface to avoid confusion and frustration.
- Limited size: Holograms are limited in size, which can reduce the realism and immersion of the experience.
- Cost: Holograms can be expensive to produce. It’s worth noting that creating and experiencing holograms can be a complex and technical process and may require specialized knowledge and equipment.
Holograms may require users to focus on specific visual cues or depth perception, which can increase cognitive workload. Additionally, the cognitive load may be increased with the need to process and integrate complex spatial and visual information, maintain situational awareness in 3D space, and perform tasks with limited physical feedback or real-world reference points. It is vital to not overload by trying to do all things with a Hologram.
Explore Your Options with Holography
When implementing any of these technologies, it’s important to always include a human factors engineer with expertise in cognitive analysis and ergonomics of the technology being implemented. Contact us to learn more about our holography enterprise solutions and how the future of technology can create measurable results in your team’s performance.
Stay tuned for the next post where I will explore the limitations of Volumetric Displays and follow me on LinkedIn.