Immersive Technology Showdown: Virtual Reality
Immersive technologies have revolutionized the way we interact with digital content, providing an unprecedented level of immersion and engagement. However, each technology has its own set of limitations, which can impact its effectiveness and suitability for different applications. Immersive technologies are rapidly evolving and gaining popularity in various industries. Virtual reality (VR), augmented reality (AR), mixed reality (MR), holograms, volumetric displays, 360 video, scent generators, and 3D audio are some of the most common immersive technologies in use today. While these technologies have immense potential, they also have limitations that must be considered before implementation.
In the previous blog, we discussed the history and use cases of immersive technology. In this article, we’ll explore and evaluate the limitations of VR training. In many cases, people are excited to use new technology but don’t understand the limitations and how it can impact successful implementation. Each immersive technology has its own physical limitations and cognitive workload considerations that instructional designers and product developers must be aware of. It is important to take these limitations into account to ensure that immersive technologies are used safely and effectively.
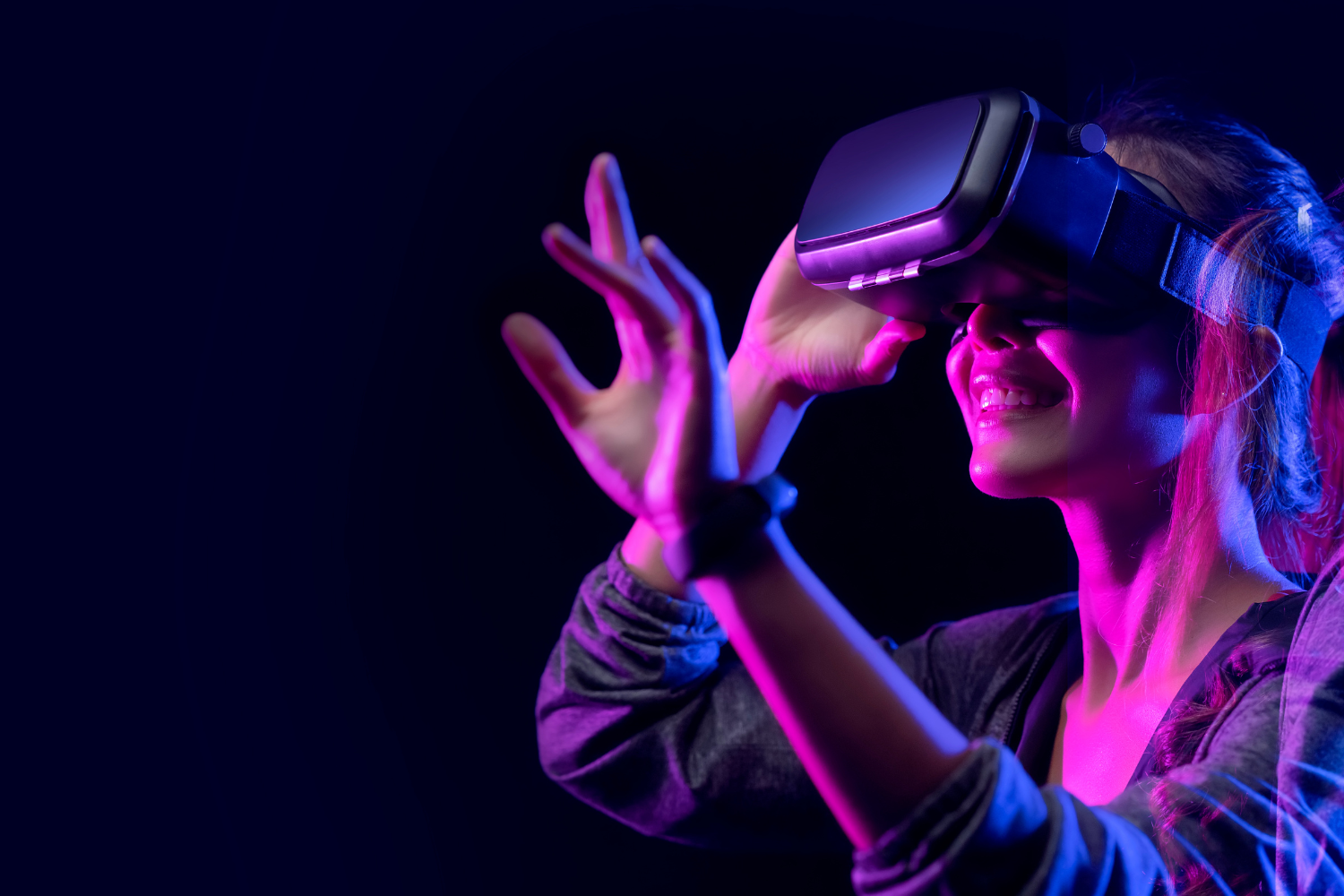
VR technology offers a fully immersive and interactive experience, where users can be transported to a computer-generated environment. However, the limited field of view and resolution of current VR displays can result in a disconnect between the virtual and real world, causing motion sickness and discomfort for some users. Furthermore, advanced hardware requirements, including a powerful computer and specialized controllers, can be a challenging investment if going into the technology blind. VR technology is best suited for applications such as training and simulations, where a high degree of immersion is necessary.
VR Hardware Considerations
VR technology requires users to wear a head-mounted display (HMD), which can be expensive and bulky. The HMD contains a screen that covers the user’s field of vision, creating the illusion of a fully computer-generated environment. VR often requires specialized controllers or hand-tracking technology for interaction, and users must be cautious of motion sickness. The hardware and software requirements for VR can vary depending on the application, with higher-end systems costing thousands of dollars. However, as technology continues to improve, VR is becoming more accessible and affordable.
Field of View (FOV)
Despite its immense potential, VR technology has several limitations that currently hinder its widespread adoption. One of the most significant limitations is the limited field of view (FOV) and resolution of current VR displays, which can result in a disconnection between the virtual and real world. The FOV is the extent to which the display can present the virtual environment, and it is often limited to around 110 degrees horizontally and 90 degrees vertically. This can cause the user to feel as though they are looking through a tunnel, which can be disorienting and detract from the sense of immersion. Similarly, the resolution of current VR displays is lower than that of traditional monitors or televisions, which can result in a pixelated or blurry image that can cause discomfort and nausea for some users.
Motion Sickness and VR
Another limitation of VR technology is the potential for motion sickness, which can occur when the virtual environment does not match the user’s physical movements. This can cause discomfort, disorientation, and even vomiting in some users. Motion sickness is more likely to occur in applications where the user is required to move rapidly or turn quickly, such as in fast-paced games or simulations. To mitigate this, VR developers often use techniques such as smoothing or reducing movement speed to make the virtual environment more comfortable for users.
Eye Strain and Fatigue
The close proximity of the VR display to the user’s eyes can cause eye strain and fatigue, leading to discomfort and reduced visual acuity. Immersive technology can exacerbate these issues. According to Essilor, the VR headsets contain two small LCD monitors, each projected at one eye, creating a stereoscopic effect that gives users the illusion of depth. The proximity of the screens to the user’s eyes has shown some cause for concern for prolonged usage.
Additional limitations include:
- Limited social interaction: VR can be isolating, limiting social interactions and collaboration between users and decreased awareness of surroundings
- User interface: The VR system should have an intuitive and user-friendly interface to avoid confusion and frustration.
Balancing the Cognitive Workload
The immersive and interactive nature of VR can be mentally demanding and increase cognitive workload. This can be especially challenging for users who experience motion sickness or disorientation in the virtual environment, as they may need to devote additional mental effort to maintain their balance and orientation. Then adding navigating unnatural menus and controls within the virtual environment can further increase the user’s cognitive workload. Cognitive workload can further be increased by the need to process and respond to multiple sensory inputs (visual, auditory, haptic), navigate a complex virtual environment, and perform tasks with limited physical feedback. The age of the user population can have a drastic impact on the ability to manage the cognitive workload. Older populations did not grow up with this digital technology and find it unnatural; whereas younger populations have had more exposure their whole life and find it less taxing.
Some strategies to mitigate these challenges may include:
- simplifying the interface and controls
- providing clear visual cues and feedback
- reducing the cognitive load of individual tasks
- allowing breaks or rest periods to reduce mental fatigue
Industry Considerations for Implementing Virtual Reality
Based on the limitations of VR, it may not be the best choice for certain applications. For example, if the user’s comfort is a priority, VR may not be the best choice as some users may experience motion sickness and discomfort due to the limited field of view and resolution of current VR displays. Furthermore, if the application does not require a high degree of immersion, such as simple training or education, other technologies such as 360 video or augmented reality (AR) may be more suitable and cost-effective options.
VR has found success in:
- Gaming and entertainment: VR allows players to immerse themselves in virtual worlds and interact with them in ways that are not possible with traditional gaming.
- Training and simulations: VR can be used to simulate dangerous or complex situations in a safe and controlled environment, allowing for more effective training.
- Healthcare and therapy: VR can be used for pain management, exposure therapy, and rehabilitation.
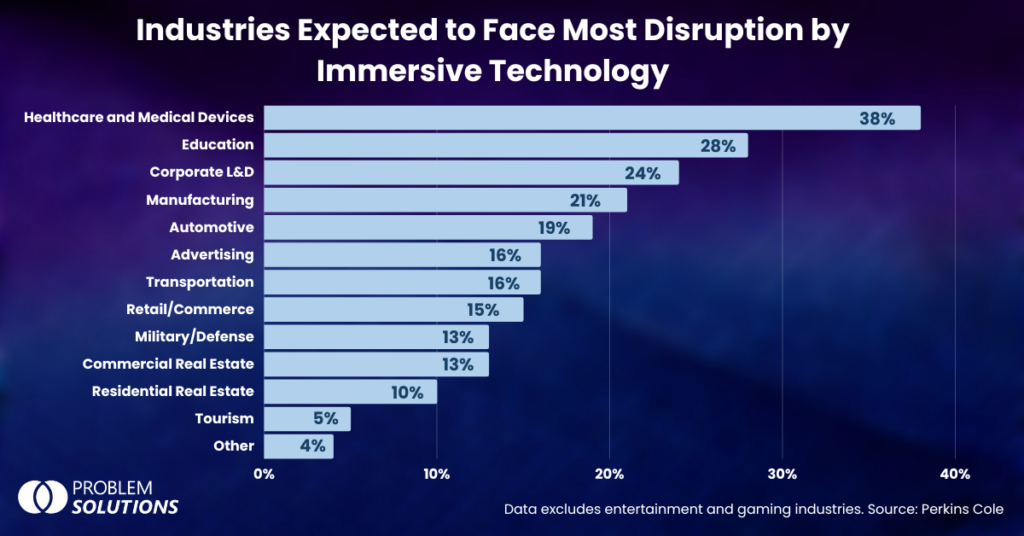
Overall, despite its limitations, VR technology remains a valuable tool for applications that require a high degree of immersion, such as training and simulations. As technology continues to improve, VR is becoming more accessible and affordable, which may help to expand its use in other applications such as entertainment and education. However, developers must continue to address the limitations of VR, such as motion sickness and limited FOV, to ensure that users have a comfortable and immersive experience.
Exploring Your Options with Virtual Reality Training
When implementing any of these technologies, it’s important to always include a human factors engineer with expertise in cognitive analysis and ergonomics of the technology being implemented. Contact us to learn more about our virtual reality training enterprise solutions and how the future of technology can create measurable results in your team’s performance.
Stay tuned for the next post where I will explore the limitations of Augmented Reality and follow me on LinkedIn.






