A Beginner's Guide to Entering the Immersive World
In recent years, the term “immersive technology” has gained popularity and is becoming a buzzword in the field of education, simulation, and training. In this beginner’s guide, we will define immersive technology, discuss the types of immersive technology available, review the brief history and evolution of immersive technology, and explore the potential benefits and applications.
Immersive technology describes a range of technologies that enable users to be transported into an artificial, simulated world, or that augment their real-world experience. It is designed to immerse the user in a computer-generated environment, creating a sense of presence and engagement that can be difficult to achieve with other media.
Immersive technology takes on many forms including virtual reality (VR), augmented reality (AR), mixed reality (MR), holograms, and 360-degree video. Each of these technologies creates a unique immersive experience and has specific applications and benefits. The key to immersive technology is the ability to engage the human senses and create an environment that allows the learner to dispel disbelief.
Common Immersive Technologies
-
Virtual reality (VR) technology uses head-mounted displays to transport users to a fully computer-generated environment. Users can interact with this environment using specialized controllers or hand-tracking technology. VR technology is primarily used for training, simulations, and entertainment applications.
- Augmented reality (AR) technology overlays digital information in the real world, typically using a smartphone or tablet camera. The development of AR headwear is still ongoing in the market. This allows users to see and interact with virtual objects as they appear in the real world. AR is particularly useful for education, marketing, and gaming applications.
- Mixed reality (MR) technology combines elements of both VR and AR, allowing users to interact with digital objects in a real-world environment. This technology is typically used for training, education, and product design applications.
- Holograms are 3D images that are typically created using laser technology, but other methods are currently in development. They can be viewed without the need for special glasses or headsets and provide a highly realistic experience. Holograms are used in a variety of applications such as entertainment, marketing, and education.
- Volumetric displays come in different forms. Typically, they use multiple two-dimensional images or frames to create a three-dimensional image or object that can be viewed from any angle. This technology creates a three-dimensional image by projecting a series of images or "slices" onto a rotating display medium, such as a spinning mirror or cylinder. As the display medium rotates, the images are updated to create a 3D image or object that can be viewed from different perspectives. Another type of volumetric display is an LED wall (seen below). The LED lights display different colors and brightness levels independently, which allows the wall to create the illusion of depth and perspective. As the viewer moves around the display, the image appears to change in perspective, just like a real object. Both display types offer a more natural and intuitive way to visualize complex 3D data, making them useful in fields such as engineering and architecture where spatial understanding is critical.
- 360 video is a type of video that allows the viewer to look in any direction, giving the impression of being present in the scene. It is typically recorded using a special camera rig that captures a full 360-degree view. The viewer is able to control the viewing direction and watch the video from multiple perspectives. 360 video is commonly used in applications such as virtual tours, marketing, and education.
- Scent generators are devices that emit scents to enhance the immersive experience. They are often used in applications such as gaming, entertainment, and marketing. By adding scents that are related to the environment or activity being simulated, scent generators can provide a more complete and realistic experience.
- 3D audio is a technology that allows sound to be positioned in a three-dimensional space, creating a more immersive experience. It simulates the way we hear sound in the real world, providing a more natural and realistic listening experience. 3D audio is commonly used in applications such as gaming, virtual reality, and music production.
History of Immersive Technologies
The history of immersive technology dates back to the 19th century when the stereoscope was invented, a device that allowed people to view images in 3D. Since then, technology has rapidly advanced, leading to the creation of more advanced immersive technology such as head-mounted displays (HMDs), holograms, and 360-degree video.
HMDs have been around since the 1960s, but it wasn’t until the 1990s that they became commercially available. The first HMDs were bulky and expensive, but advancements in technology have made them more compact and affordable. Today, HMDs are widely used in gaming and virtual reality (VR) experiences.
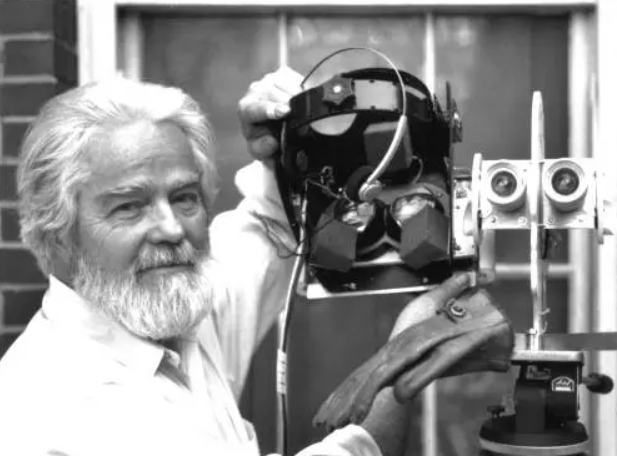
Eric Howlett, pioneer in virtual reality and inventor of LEEP (Large Expanse, Extra Perspective) technology, which serves as the basis of most VR headsets today.

Holograms, first invented in the 1940s, have also made significant advancements over the years. The first holograms were static and could only be viewed from one angle. Today, holograms can be viewed from multiple angles and can be interactive, allowing users to manipulate and move objects in real-time.
360-degree video and photogrammetry have become increasingly popular in recent years, thanks in part to advancements in camera technology. 360-degree video allows viewers to experience a scene from any angle, creating a more immersive experience. This technology is commonly used in virtual tours, documentaries, and other applications where the viewer wants to feel like they are a part of the experience.
From a technical perspective, immersive technology has come a long way. High-resolution displays, improved graphics, and better tracking systems have all contributed to more realistic and immersive experiences. In addition, advancements in artificial intelligence and machine learning have enabled immersive technology to become more intelligent and responsive to user interactions.
Defining Uses of Immersive Technology
Today, immersive technology has a wide range of applications, including entertainment, education, training, and marketing. In entertainment, immersive technology is used to create more realistic gaming experiences and to enhance movies and television shows. In education, it is used to create simulations that allow students to practice skills in a safe environment. In training, it is used to create realistic scenarios that prepare employees for real-world situations. In marketing, it is used to create interactive experiences that engage consumers and provide a more memorable experience.
The benefits of immersive technology are vast and varied. Immersive technology can improve engagement, retention, and transfer of knowledge. It provides learners with a safe environment to practice and develop skills, reducing the risk of errors and accidents. Immersive technology can also increase accessibility and democratize learning, making education and training available to a wider audience. In healthcare, immersive technology can help diagnose and treat patients, reducing costs and improving outcomes. In tourism, immersive technology can provide an experience that is not possible in real life, enhancing the overall customer experience.
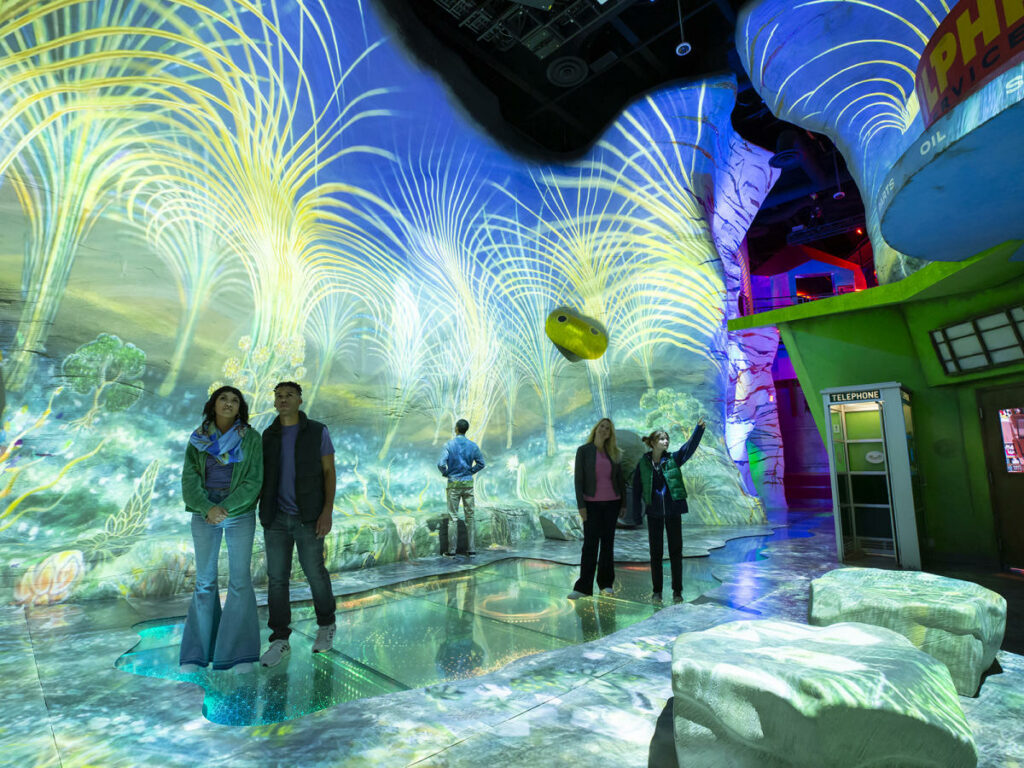

Moreover, immersive technology can significantly impact industries such as architecture and engineering by allowing professionals to design and create in 3D, providing a more accurate representation of the final product. In the entertainment industry, immersive technology has transformed the way movies, video games, theme parks, and art exhibits (such as Las Vegas’ Meow Wolf – pictured) are experienced by blurring the lines between reality and virtual reality. It enables users to be fully immersed in the story and environment, creating a truly unique and unforgettable experience.
Additionally, immersive technology has the potential to improve mental health by providing exposure therapy for individuals with anxiety disorders, phobias, and post-traumatic stress disorder (PTSD). It also allows individuals with mobility issues to participate in activities and experiences that may have been previously inaccessible.
Stay Tuned
Stay tuned. In this series, we are evaluating immersive technology, exploring its limitations, sharing how to evaluate and validate it, and discussing emerging trends.






